From Factory Floors to Modern Workplaces: The Evolution of Industrial Working Conditions

Photo by Pablo Fernández on Unsplash
Introduction: Industrial Working Conditions Through History
Industrial working conditions have undergone dramatic changes since the dawn of the Industrial Revolution. Early factories were notorious for their hazardous environments, long hours, and exploitation of labor-including children. Over time, worker advocacy, legislation, and technological advances have contributed to safer, fairer workplaces. This article explores the evolution of industrial working conditions, examines pivotal moments in labor history, and provides actionable guidance for accessing modern worker protections and resources.
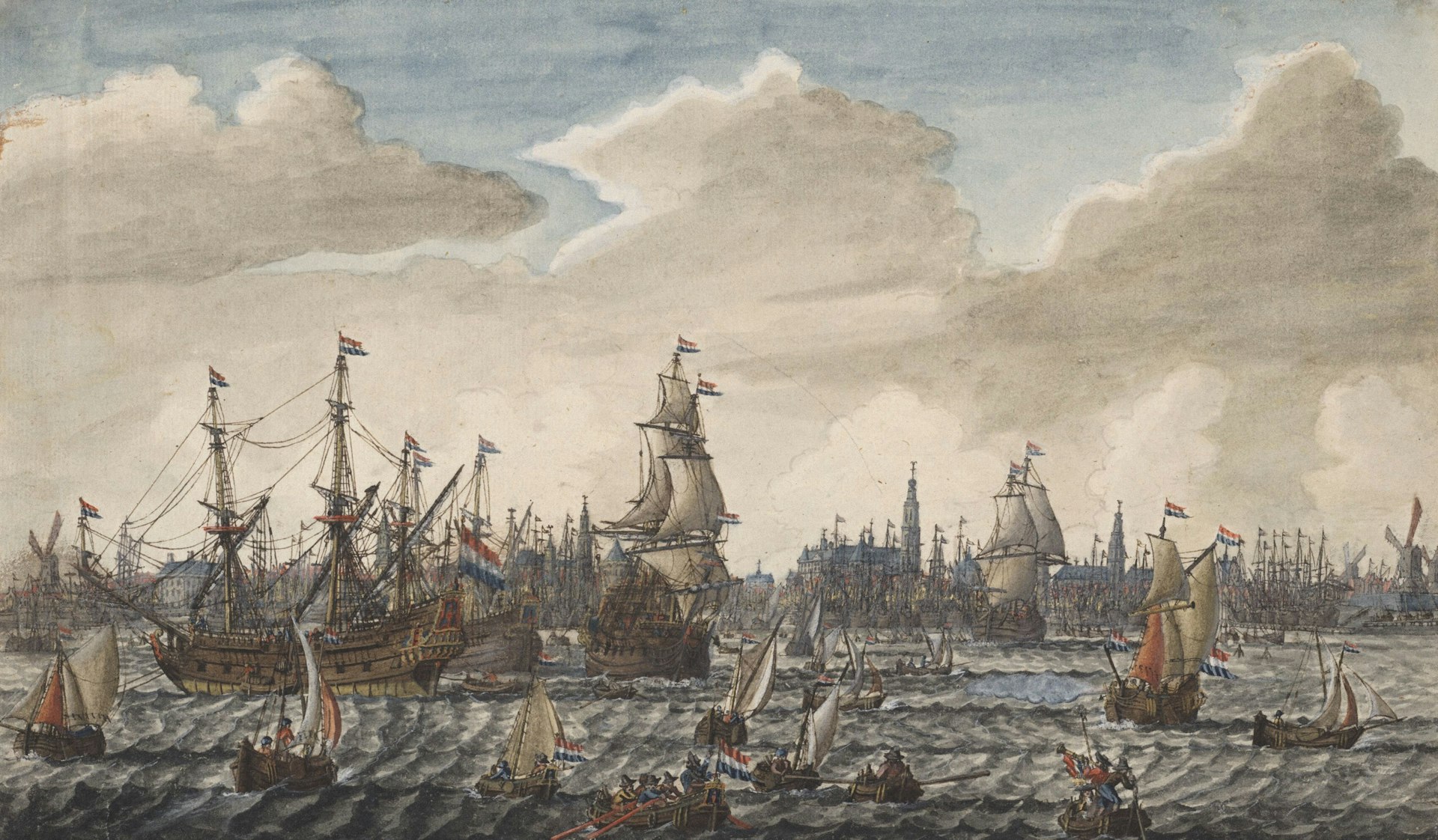
Early Industrial Era: Hazardous Beginnings
The Industrial Revolution (circa 1760-1840) marked a shift from agrarian economies to factory-based production. Workers faced long hours , often 12-16 hours per day with minimal breaks, in dangerous settings such as textile mills, coal mines, and steel plants. Child labor was widespread, and physical discipline was a common management tool. Injuries, chronic health problems, and fatalities were frequent, with little to no compensation or recourse for employees [1] .
Most workers had few alternatives, forcing them to endure poor conditions to earn a livelihood. The lack of labor rights enabled factory owners to maximize profits at the expense of worker safety and dignity. Real-world cases included deadly factory fires, machinery accidents, and occupational diseases.
The Rise of Labor Movements and Early Reforms
By the late 19th century, the growing labor movement began to challenge exploitative practices. Notable events included the formation of the Greenback Labor Party and the International Labor Union in 1878, and pivotal strikes such as the Newsboys Strike (1899) and the Passaic Textile Strike (1926) [2] . These actions raised public awareness and pressured governments to introduce reforms.
Massachusetts led the way in 1877 with the Factory Acts, which set the precedent for workplace inspections and safety protocols. These included requirements for equipment safety, ventilation, and cleanliness. However, enforcement was often weak, and unsafe working conditions persisted for decades [5] .
Major Turning Points: Tragedy and Reform
Some reforms followed tragic events. The 1911 Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in New York City killed 146 workers-mostly young immigrant women-due to locked exits and inadequate safety measures. Public outrage over such incidents led to landmark legislation improving fire safety, building codes, and worker protections [5] .
Other major strikes, such as the “Bread and Roses” strike in Lawrence, Massachusetts (1912), involved thousands of men, women, and children demanding better wages and safer conditions. These actions catalyzed the creation of the Department of Labor in 1912 and the appointment of the first Secretary of Labor in 1913 [3] . The founding of the International Labor Organization in 1919 marked a global commitment to improving working conditions [3] .
Modern Era: Legislation, Safety, and Worker Rights
Throughout the 20th century, additional reforms further protected workers. The Railway Labor Act (1926) required collective bargaining and prohibited discrimination against union members [2] . The rise of unions, such as the AFL-CIO, played a crucial role in negotiating better wages, benefits, and workplace safety [4] .
Legislation such as the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA, 1970) established comprehensive national standards for workplace safety. Employers became legally obligated to provide safe environments, conduct regular safety training, and report workplace injuries. Continued union advocacy and regulatory oversight have helped reduce workplace injuries and fatalities, although challenges remain in certain industries and regions.
Accessing Worker Protections and Resources Today
Modern industrial workers benefit from a robust array of protections and support services:

Photo by Alpha Perspective on Unsplash
- Union Membership: Joining a union can provide collective bargaining power for safer conditions and better pay. Many unions have dedicated safety officers and legal support. To find a union relevant to your industry, search for organizations such as the AFL-CIO or the United Steelworkers.
- Legal Protections: Workers can file complaints with OSHA if safety standards are violated. Visit the official OSHA website or contact their regional offices for guidance on filing claims and accessing safety resources. You may also consult your local Department of Labor office for information on wage and hour laws, discrimination protections, and other rights.
- Educational Resources: Many labor history societies and museums offer educational programs and materials on workplace safety and rights. Examples include the Illinois Labor History Society and the Seattle Civil Rights and Labor History Project [4] . You can search for these organizations by name or contact your local historical society for more information.
- Training and Certification: Workers seeking up-to-date safety training can enroll in OSHA-certified courses, which are often available through technical colleges or online platforms. These courses cover hazard identification, emergency protocols, and legal rights.
Step-by-Step Guidance:
- Identify your industry and region-specific labor organizations or unions. Start by searching for “[your industry] union” or “labor history society [your state].”
- Review your rights under OSHA and Department of Labor regulations. You can search “OSHA worker rights” or “Department of Labor wage laws” for official resources.
- If facing unsafe conditions, document the issue, gather evidence, and contact your union representative or OSHA regional office for assistance.
- Participate in workplace safety training and encourage your employer to host regular safety briefings.
- Utilize available educational resources to stay informed about historical and current trends in industrial working conditions.
Alternative Approaches: In non-union workplaces, workers may organize informal committees to address safety concerns or collaborate with outside safety consultants. Advocacy groups and legal aid organizations can also provide support for workplace rights and injury claims.
Challenges and Ongoing Issues
Despite improvements, some challenges persist. Hazardous work still exists in industries such as mining, construction, and agriculture. Gig economy workers and contract laborers may lack access to traditional protections. Language barriers, fear of retaliation, and lack of awareness can impede access to rights and resources.
Solutions include ongoing education, advocacy, and coalition-building among workers. Employers are encouraged to foster transparent communication and regularly update safety protocols. Workers can also seek out community organizations or legal aid for support in navigating complex labor disputes.
Key Takeaways
From the perilous beginnings of factory labor to the regulated environments of today, the evolution of industrial working conditions reflects the persistent struggle and advocacy of workers worldwide. By understanding historical challenges and leveraging modern protections, today’s workers can secure safer, fairer workplaces and continue the legacy of labor reform.
References
- [1] FactoryWorkingConditions.com (2023). The Evolution of Factory Working Conditions.
- [2] Wikipedia (2024). Timeline of Labour Issues and Events.
- [3] SEIU 721 (2018). Timeline of Labor History.
- [4] AFL-CIO (2024). Our Labor History Timeline.
- [5] Vigilife (2023). A Timeline of Workplace Safety in the U.S.
MORE FROM resultsdiscount.com